The accuracy of manufacturing costs is essential for managing a company, as businesses use this data as an indicator to support many strategic decisions. An example that helps us see how important it is, is the Profit Margin.
The Importance of Accurate Cost Calculation
The analysis of the Profit Margin on products evolved as industries and markets expanded around the globe. It ceased being freely defined by the company [Costs + Profit Margin = Sale Price] and is now determined based on the power of consumers [Sale Price - Costs = Profit Margin]. In this sense, the higher the company's manufacturing costs, the lower the profit margin. This can dictate the company's survival in the sector, revealing the exceptional importance of correctly determining these costs.
The concept of Manufacturing Costs is recognizable as the set of all costs a company incurs during the process of transforming raw materials into finished products. There are three components to these costs: Direct Materials Costs, Direct Labour Costs and Overhead Costs.
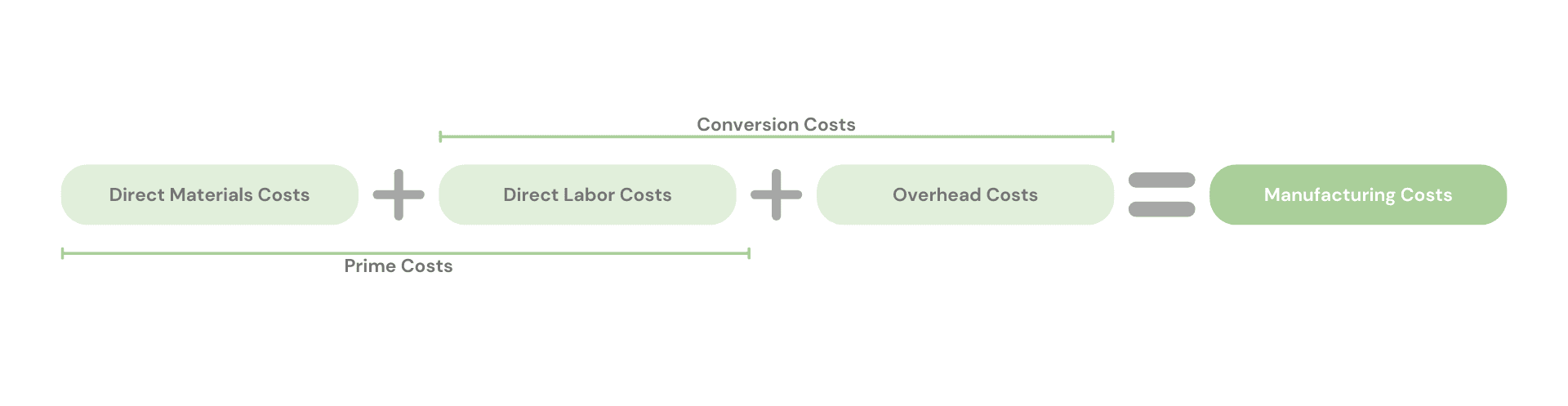
- Direct Materials Cost: As the name implies, this represents the value of all the basic goods used to obtain the finished product. Their incorporation is physical and easily observable.
- Direct Labor Cost: It comprises all expenses associated with the remuneration of individuals directly involved in manufacturing the products. This is the total salary amount, as well as charges a company incurs related to this expense. Generally, to divide these charges evenly over the business year is applied at a theoretical rate.
- Overhead Costs: These are more complex to define since they include all other costs incurred in the manufacturing
operations that are not raw materials or direct labor. In other words, these are the common manufacturing costs
throughout the entire factory. Some examples:
- Indirect labor, which contains the remuneration and charges of the personnel who support the work
- Depreciation of factory equipment
- Insurance of equipment and production facilities
- Rent from industrial facilities
- Subsidiary materials
After determining these three cost categories, it is possible to calculate:
- Prime Cost, by isolating all the direct costs of the products
- Conversion Costs, which demonstrate all the costs necessary to convert the raw material into finished products
In this way, the sum of the three components results in the sum of all costs applicable to manufacturing that occurs during a given period.
Odoo & Manufacturing Costs
Let's now jump into Odoo and see how to treat these costs and have an easy reference along the manufacturing period.
Example case: manufacturing of a Chair.
On the shopfloor, the process starts with grouping all the components that belong to the same chair at Parts Station. Once the first operation is complete, the parts are assembled, transforming the raw materials into a Chair. After polishing the Chair, at the Finish Station the finer details, such as painting, will be applied accordingly to the customer's request.
The steps to reproduce this example in Odoo are:
Step 1: Create
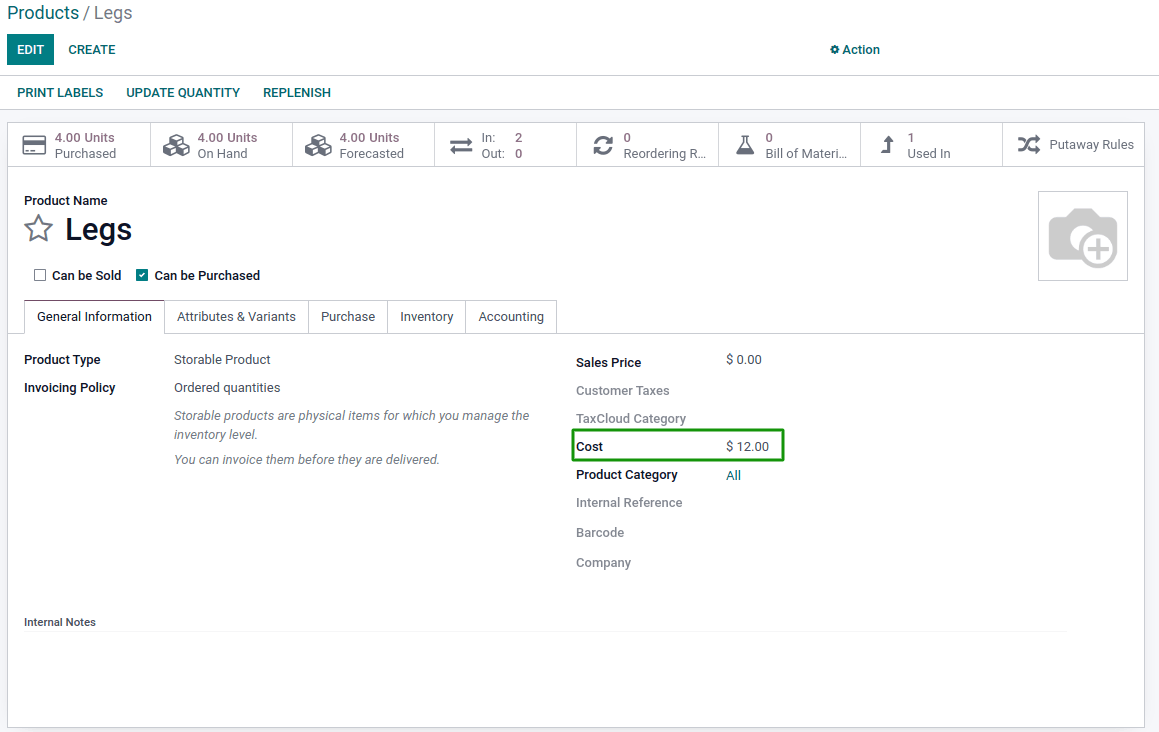
First, create the product, Chair, with a manufacturing route and all components [Legs, Backboard, Seat] you need to produce it. When creating the components, take care when defining the cost because the system will incorporate the calculation of the Chair industrial cost. Note: if the company policy is the average cost (AVCO), the Cost field will automatically compute along with the purchase orders introduced on the database.
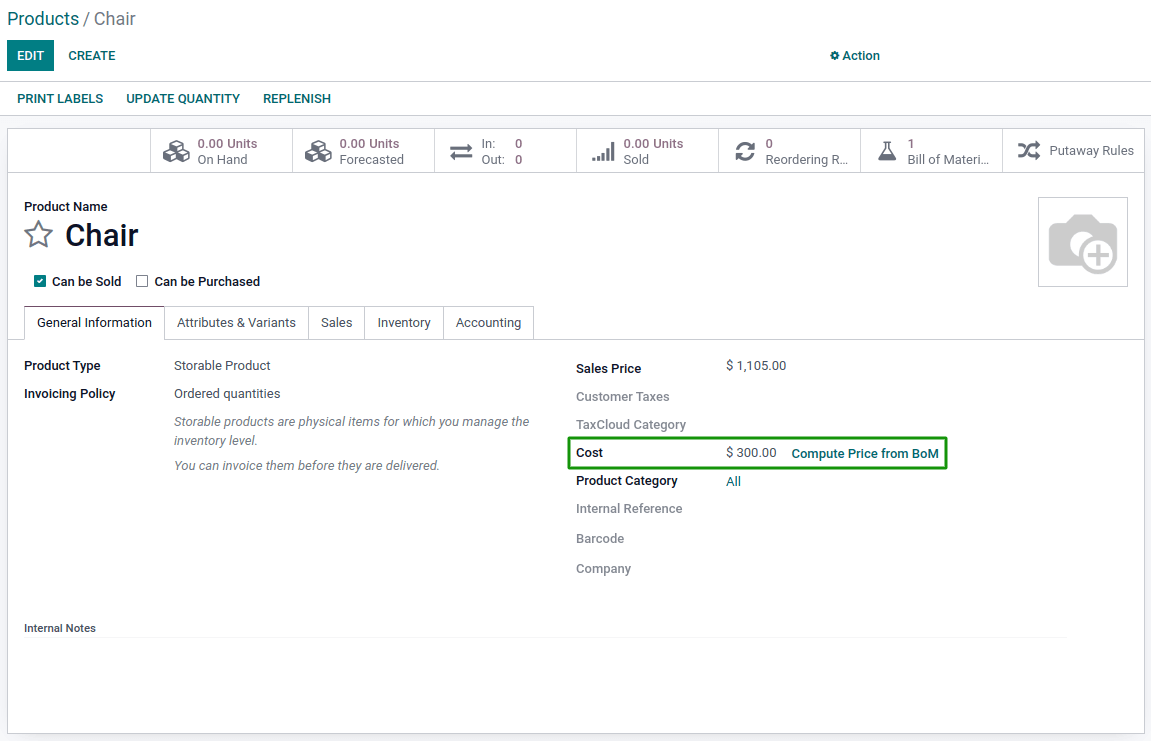
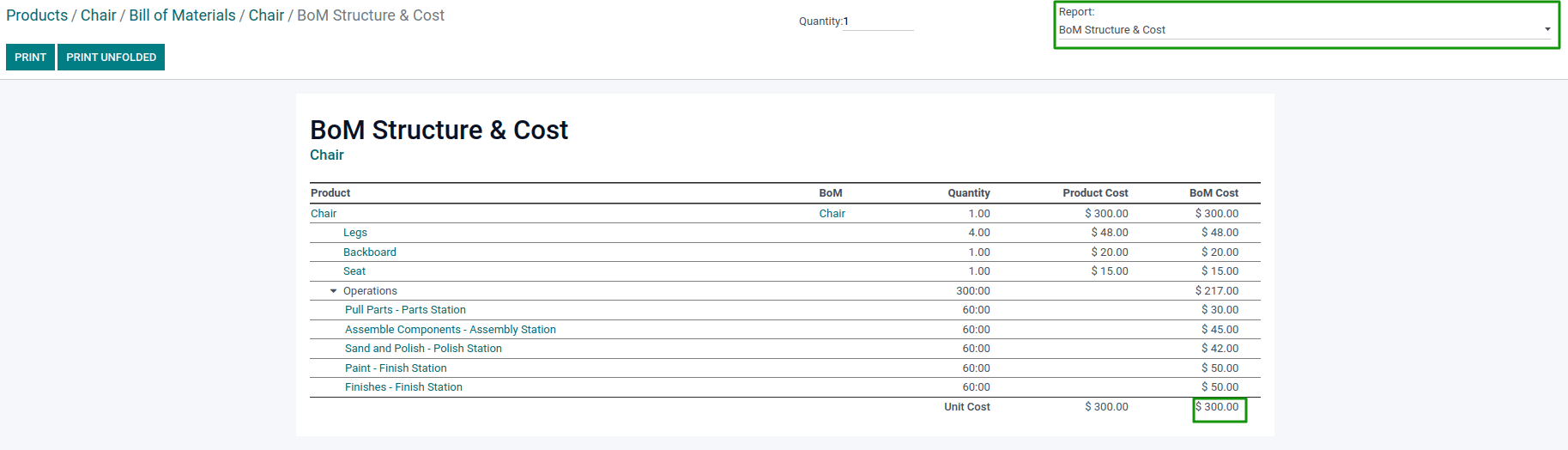
Concerning the cost of the finished product, Odoo can also compute it based on the structure of the Bill of Materials (BoM). This includes the components plus the operation costs.
Learn more About Odoo and Manufacturing
Step 2: Work Centers
Secondly, create and configure the Work Centers.
In this case, the Chair shop floor is separated into stations:
- Parts
- Assembly
- Polish
- Finish
In each of them, it’s essential to set the cost per hour and the time efficiency. They’re important because the system uses those fields to calculate the cost of the chairs. The Time Efficiency field is used to calculate the expected duration of a work order at a specific Work Center. So, as long the efficiency increases, the operation’s duration will decrease in the same proportion and vice-versa, impacting the BoM operation cost. To estimate the Work Center's cost per hour, one must consider all the expenses related to them. This can include electricity, fuel, 100% of the operator's salary, a percentage of the production manager's salary and more. So, when setting up Work Centers, the costs used are estimated and need to be revised periodically.
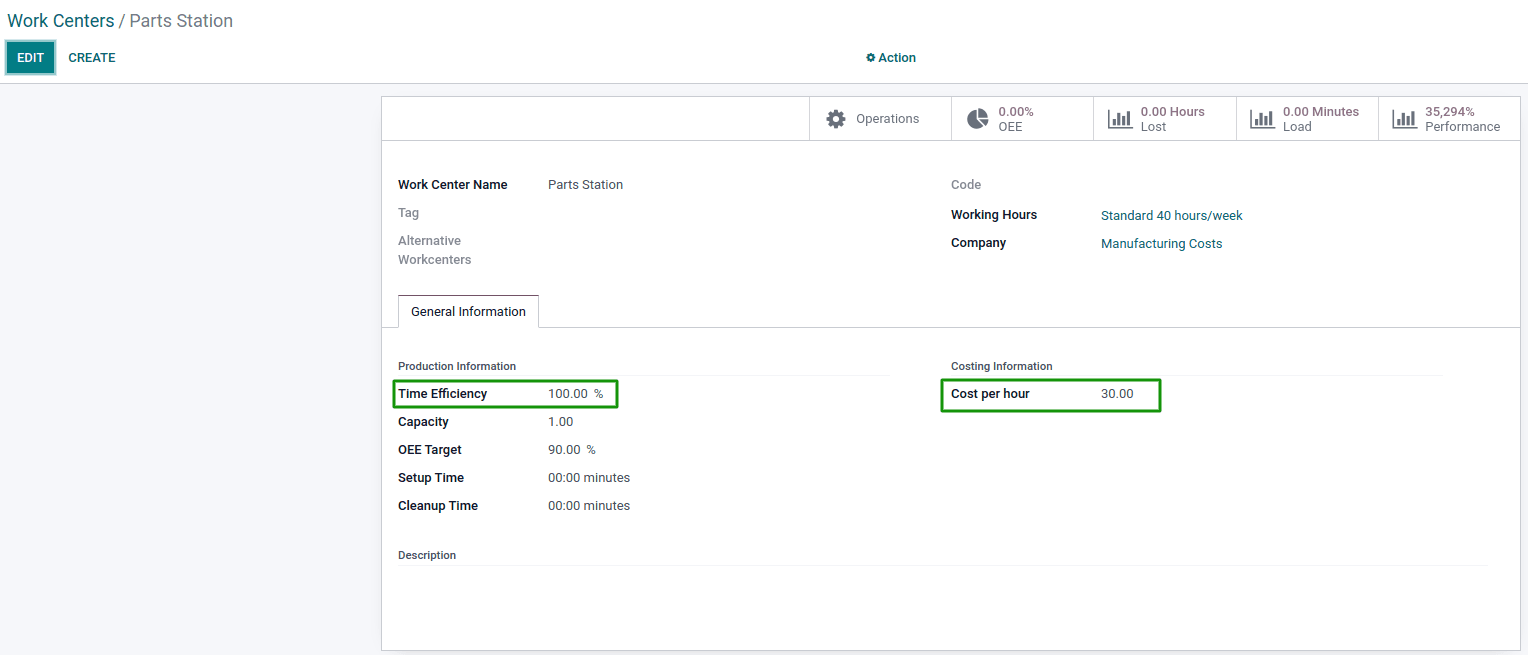
Step 3: BoM
Next, you can proceed with the structuration of the BoM for the manufactured product. You’ll assign the components used to manufacture the product, and create the operations that will be carried out at the different Work Centers.
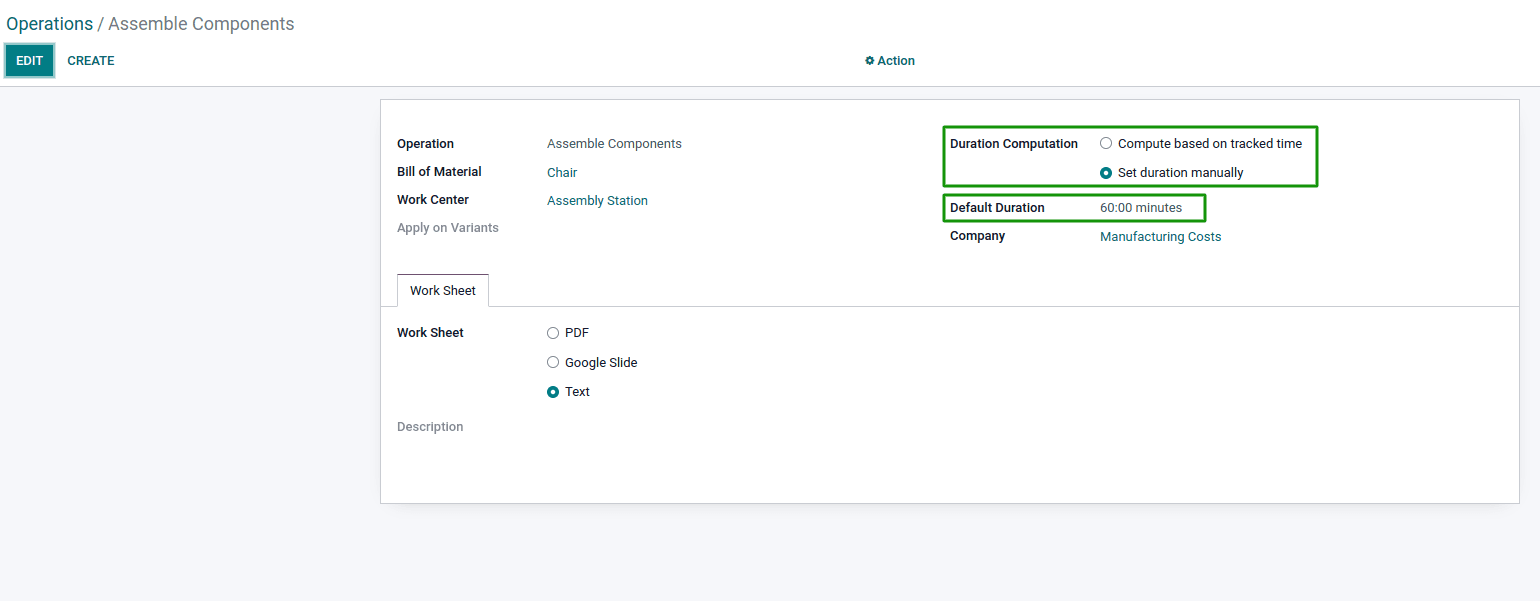
Focusing on the operation duration, there are two options to define the time spent:
- Set it manually
- Calculated based on an average from a specific range of work orders.
After setting up all the data and managing the daily work in the factory, it is time to do some analysis.
Step 4: Analysis
To know how many hours your Work Centers have worked, go to Work Centers View and add the Productive Time column on the view. Note that the information in this field is the sum of productive hours over the last month.
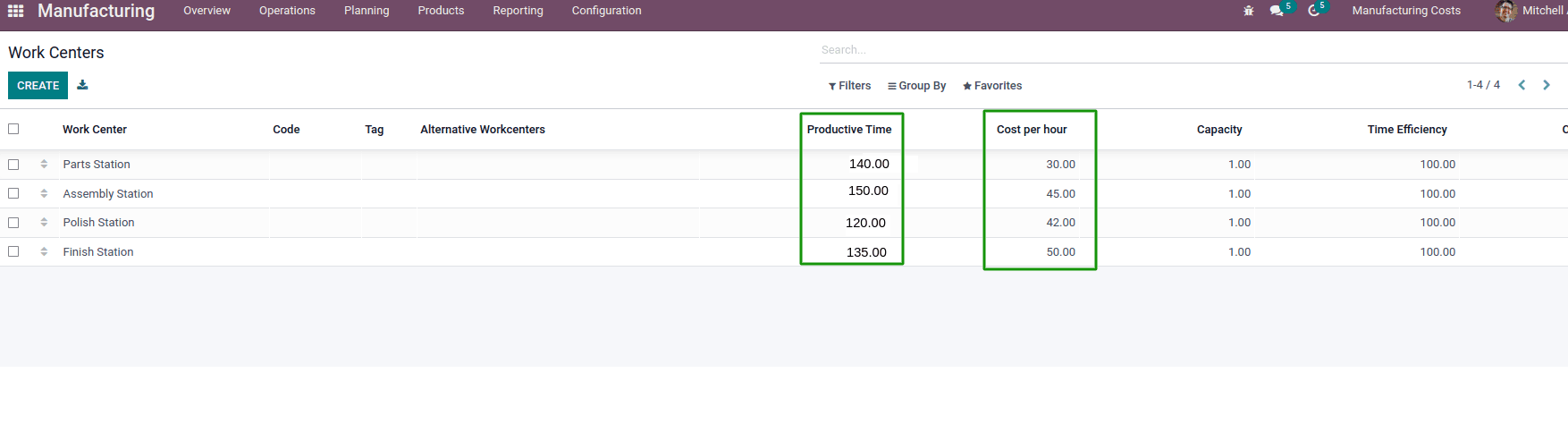
In Summary
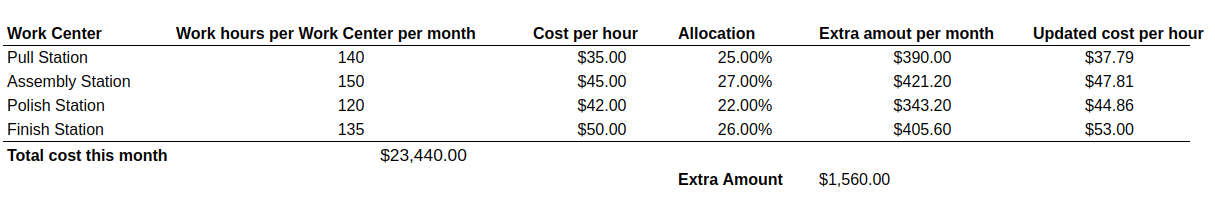
At the end of the month, the Work Centers’ estimated costs represent $23,440.00. However, if assuming an actual monthly cost of $25,000.00, you must adjust the Work Centers’ costs with an additional amount of $1,560.00. You need to consider the company’s policies and criteria regarding the allocation of this value. For example, you can divide it equally between all the Work Centers, or assign a higher percentage to ones with more worked hours. When using the second cost allocation criterion, the Work Centers’ costs are now more realistic:
It’s therefore possible to accurately calculate costs, assign it to Work Centers and allow Odoo to facilitate data integration. Now, if you adopt an automatic inventory valuation [defined in the product categories] and ruled stock management, the system will generate all journal entries in real-time. This provides a current balance for the Cost of Goods Sold [COGS] account, and an up-to-date inventory of the company. Also, the cost structure specified on each Bill of Material allows the company to have individual information about the Manufacturing Costs for each product. This is helpful and advantageous for deeper and more elaborated analysis. This shows yet another way that Odoo helps companies obtain enough data to support better decisions. And that impacts a company's success. Want to learn more about this or other Odoo benefits?